Teaching Literary Analysis
Guide students through the five steps of understanding and writing literary analysis: choosing and focusing a topic, gathering, presenting and analyzing textual evidence, and concluding.
Your content has been saved!
Go to My Saved Content.Literary analysis is a vital stage in the development of students' critical thinking skills. Bloom's Taxonomy illustrates that analysis should come at the fourth level, right after comprehension and application. What this means is that students must be able to understand and describe the text before they are able to analyze its elements.
Teaching literary analysis is often a daunting and overwhelming task. After all, it is essentially guiding students slowly through the process of critical thinking and understanding literature. That’s not a simple undertaking. Most importantly, with so many ways to go about doing it, where to begin?
To guide students toward discovering literature all on their own, the steps of this process need to be introduced in a simplified form. It's very important for the student to understand that literary analysis is indeed a process where there is no right or wrong answer. This empowers students to be passionate about their topics and, most importantly, encourages them to look beyond the words on the page.
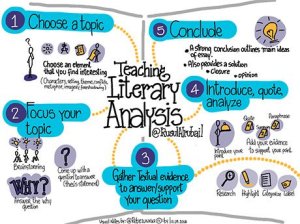
1. Choose a Topic
Some students need guidance when choosing a topic, but others have ideas that they would like to explore. Topics can be divided into the main literary elements:
- Characters
- Themes
- Literary devices
- Setting
- Narrative.
2. Focus the Topic
Here is where many students will need to do a lot of brainstorming, outlining, and specific thinking about the element on which they would like to focus.
- The brainstorming process involves mapping out the different aspects of the chosen element.
- Make a choice by narrowing down the selection and focusing the ideas.
- Come up with a question to answer (thesis statement): What do you want to explore about the topic? Why does it stand out to you?
- Answer the "why" question. Instead of letting students simply describe the text, "why" pushes them to analyze and even synthesize. This aspect is vital to student understanding, as most of the time a teacher is able to identify a relevant thesis related to modern-day issues and concepts. Here is where real-world application, analysis, and synthesis can begin to form in this piece of writing.
3. Gather Textual Evidence
Collecting material to answer or support your question is often a time-consuming stage, because most of the close reading will occur here. It's important for students to know that they're allowed to research the topic or text before starting to write. Many students feel that they should not be using Google or Wikipedia to research their texts. Here is where the teacher can have an honest discussion about digital citizenship, and how to tell credible academic sources from non-credible ones.
Show students that close reading and gathering evidence doesn't have to be a mundane, one-dimensional task.
- Identify common themes, repetitions, and patterns.
- Categorize elements, tone, and narrative style.
- Highlight characterization, setting, and foreshadowing.
- Label character types, symbols, and metaphors.
4. Introduce, Evidence, Analyze
Learning through writing and literary analysis happens through stages (see Bloom's Taxonomy). At this stage of writing, students have already accomplished remembering, understanding, and applying. Next comes analysis.
Introduce
Students should introduce their point in one or two clear topic sentences. Next, it's important to provide evidence that supports the main topic in order to convince the reader of the stated point of view. There are a few ways students can add their evidence.
Evidence
- Quotation: When providing evidence word for word from a primary or secondary source, students should be reminded to use quotation marks only if the words have not been altered.
- Summary: Students summarize a piece of evidence by restating it in a shorter form using their own words.
- Paraphrase: Students explain a piece of evidence using their own words.
At this stage, it's important to use the lesson as a reminder to cite and give credit for words and ideas that belong to others. A conversation with the class about academic honesty is very important to help them understand intellectual property. This conversation will also prepare them for honesty and ethics in the real or academic world.
Analyze
This critical stage is often a learning curve for many students. It's important that the teacher helps them distinguish between descriptive writing and analytical writing. Descriptive writing answers the "who," "what," "where," and "how" questions. It often tends to summarize the text. Analytical writing, however, answers to the "why" question. When students consider the question, "Why is this point important?", it pushes them beyond mere description into ideas that are convincing, argumentative, and defend a position.
5. Conclusion
A strong conclusion outlines the main ideas of the essay, but it also works to provide a solution to a real-life problem. Students can focus on concluding with what they hope to get out of their analysis, or provide closure to the topic. Most importantly, students should seize the conclusion as an opportunity to provide their own opinion and reflection about their process of analyzing the text. The self-reflection here would be a vital key for teachers to assess the writing process and a great opportunity to provide essential feedback to the student.
Please share your own experiences in teaching students about literary analysis.
